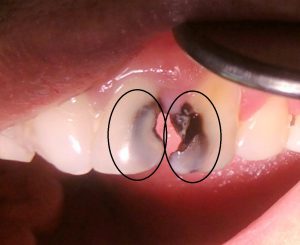
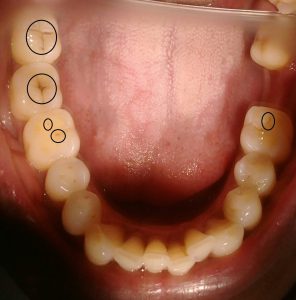
Halitosis is a common social condition that affects a considerable portion of the general population. The prevalence of halitosis is close to 50% in a few populations. Under few circumstances, this oral condition may cause embarrassment, depression and make relationships more difficult. Some studies have investigated whether the psychology of the patients might have some influence on the complaints about halitosis, or even on halitosis itself. In a study that included more than one thousand participants and self-reported halitosis, scientists have reported that poor oral hygiene and general anxiety are associated with halitosis. [1] Halitosis is divided into intraoral, extraoral, pseudohalitosis and halitophobia. Intraoral halitosis, responsible for 85% of the cases of halitosis, is subdivided into physiologic (genuine) halitosis or pathologic halitosis. Extraoral halitosis occurs when malodor appears with no oral cause, as in the case of pulmonary causes. Both patients with pseudohali...