Bacterial lesions causing ulcerative conditions in the oral cavity
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhoea
- Tuberculosis
- Leprosy
- Actinomycosis
- Noma
A coaching institution for ADC, ORE and Government dental job examinations.
You must know the properties of the materials used in dentistry to understand its function and how and why it works in oral cavity. It also helps in manipulating it. The main properties you should know about are following:
Enamel: This is the hard, calcified substance that makes the surface of a crown of a tooth.
Pulp: This is the organ at the centre of a tooth that contains blood vessels, connective and neural tissue, and cells that produce dentine-odontoblast. Blood vessels and neural tissue enter the tooth from the apex of the root.
Periodontal ligament: This is the ligament that connects a tooth, by its root, to the supporting bone.
Cementum: This is the calcified tissue on the surface of the root of a tooth, which provides attachment for the periodontal ligament.
Fissure: It is a naturally occurring crevice in the enamel.
Crown: This is the part of the tooth that is visible and is above the gingival margin.
Root: This is the part of the tooth below the gingival margin; it is connected through cementum on its surface and the fibres of the periodontal ligament to the supporting bone.
There are numerous dental numbering systems to identify teeth and their
maturity. The most commonly used system in Australia is the Federation Dentaire
Internationale (FDI) system
The FDI numbering system divides the mouth into quadrants. The first
number indicates the quadrant and whether it is a primary or secondary tooth.
The second number indicates the tooth; tooth numbering begins at the central
incisor and counts backward to the molars.
Using the FDI numbering system, for adults, the quadrants are numbered as:
1. patient’s upper right is quadrant 1
2. patient’s upper left is quadrant 2
3. patient’s lower left is quadrant 3
4. patient’s lower right is quadrant 4
For primary teeth in children, the quadrants are numbered as:
1. patient’s upper right is quadrant 5
2. patient’s upper left is quadrant 6
3. patient’s lower left is quadrant 7
4. patient’s lower right is quadrant 8
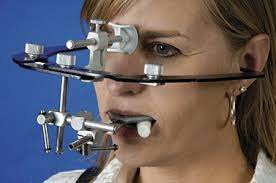 |
| Face bow-for Whip mix Arcon articulator |
Face bow is a device that is used to transfer the relationship of upper jaw to the temporomandibular joint and the skull. The use of face bow are as follows:
 |
| Face bow for Hanau Non-Arcon Articulator |
Dens invaginatus, dens in dente or tooth with in a tooth is a rare developmental anomaly. In it, the lingual pit is extended deep in to the crown or root, in later instance causing pulpitis. It is mostly seen in the maxillary lateral incisors but may be found in any anterior tooth.
 |
| Dens in Dente-lateral incisors |