Composites are tooth coloured restorative materials that are usually recommended for class III, IV and class I cavities with less or no occlusal stress and esthetics are important. Specially designed composites are used in almost 50% of class II restorations, although less durable in comparison to dental amalgam. Composites can be classified as microfilled, nanofilled, flowable, packable, all purpose and laboratory. Composites are used for provisional restorations and core build-ups and in fibre-reinforced posts.
A coaching institution for ADC examination, and Government dental jobs exam.
Composites: Properties
Properties of Composites
- Polymerisation shrinkage - should be low
- Water sorption - should be low
- Coefficient of thermal expansion - should be same as tooth
- Fracture resistance - should be high
- Wear resistance - should be high
- Radiopacity- should be high
- Bond strength to enamel & dentin - should be high
- Colour match to tooth structure - should be excellent
- Manipulation - should be easy
- Finishing and polishing - should be easy
Direct Esthetic Restorative Materials
Direct Esthetic Restorative Materials
There are four types of direct esthetic
restorative materials currently in use. They are:
- Composites
- Compomers
- Hybrid
Ionomers
- Glass Ionomers
Composites are dominating the materials used for direct esthetic restorations. Glass ionomers are primarily used for restorations of cervical eroded areas. Hybrid ionomers provide better esthetics than glass ionomers. Compomers provide improved handling and fluoride release when compared with composites.
Polysulfide Impression Materials
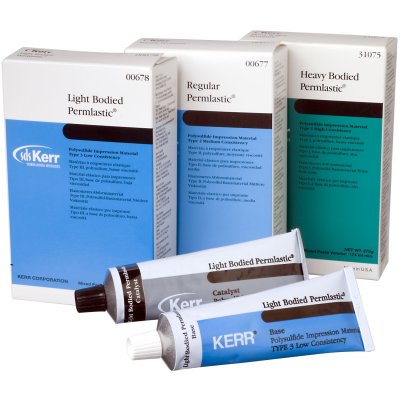 |
| Permlastic is a polysulfide, condensation-cured, elastomeric impression material in three viscosities |
Non-carious loss of tooth structure
Types, clinical features, Causes prevention & treatment
Types of tooth wear
- Abrasion
- Attrition
- Erosion
- Demastication
- Abfraction
NEET 2022-23 Exam Dates Declared by NBE for NEET-MDS UG and PG
- NEET-MDS 2023: January 8, 2023
- DNB/DrNB Final Practical Examination – June 2022: October/November 2022
- Foreign Medical Graduate Examination (FMGE) December 2022, Foreign Dental Screening Test (FDST) 2022: December 4, 2022
- Formative Assessment Test (FAT) 2022: December 10, 2022
- DNB/DrNB Final Theory Examination – December 2022: December 21, 22, 23 and 24, 2022
- Fellowship Entrance Test (FET) 2022: January 20, 2023
- FNB Exit Examination 2022: February/March 2023
- DNB/DrNB Final Practical Examination – December 2022: Feb/March/April 2023
- NEET-PG 2023: March 5, 2023
 |
| Distribution of subject wise questions in NEET MDS examination. |
Harmful Effects of Excessive Radiation
The harmful effects of the excessive dose of the ionizing radiation can be divided into two types. These are as follows:
- Deterministic effects and
- Stochastic effects
We shall discuss them one by one in detail.
Radiography: Radiation Safety
In earlier articles on radiography, you studied the effects of ionizing radiation on biological tissues. These effects can be divided into two types- Deterministic and Stochastic. Therefore, the radiation safety becomes of paramount importance white taking a radiograph.
